Enterprise-Grade Technical Best Practices Salesforce AI (Einstein + Agentforce)
1. What Enterprise AI on Salesforce Requires
Enterprise adoption of Einstein and Agentforce requires a balance of:
- Data trust (grounding, governance, unification)
- Secure autonomy (audited and bounded actions for agents)
- Scalable architecture (flows, Apex, Data Cloud, events)
- Continuous monitoring & drift detection
These components form the foundation for any AI-driven automation across customer, sales, service or IT workflows.
2. High-Level Enterprise Architecture for Salesforce AI

Key Architecture Notes
- Data Cloud = Enterprise single source-of-truth powering AI grounding.
- Grounding Layer = Knowledge Articles, Object records, policies, examples.
- Reasoning Layer = LLM-driven decision engine with prompt templates.
- Execution Layer = Flows, Apex, Orchestration for deterministic behavior.
3. Grounding Strategy for Large Organizations
1.1 Data Cloud Unification
- Use identity resolution rules to merge customer profiles across multiple systems (ERP, Web, Support, Commerce).
- Enrich profiles with behavioral and transactional data for contextual reasoning.
1.2 Knowledge Base / Policy Grounding
For AI reliability:
- Maintain a curated, versioned knowledge base.
- Add metadata tags (product, region, compliance rule) for precise retrieval.
1.3 Enterprise Grounding Pipeline

4. Security Model for Enterprise AI
2.1 Integration User Strategy
- Dedicated AI Integration User per agent or agent family.
- Enabled with:
- Minimal CRUD permissions
- Strict field-level access
- Restricted record types
2.2 Guardrails & Access Boundaries
- Limit agents from:
- Changing ownership
- Modifying financial or contractual fields
- Approving workflows without human review
2.3 Encryption & Shield Controls
- Use Event Monitoring to track:
- AI-run API calls
- Autonomous updates
- Unusual data access patterns
5.Prompt Engineering, Agent Design & Reasoning Frameworks
- Prompt Engineering Framework for Enterprises
Use the R-A-G-E model:
Role • Actions • Grounding • Expectations
1.1 Prompt Template Structure
- Role: “You are a Salesforce Service Agent…”
- Allowed Actions: “You may only update Case fields A,B,C…”
- Grounding: Include KB articles + examples + schemas.
- Output Schema: Always JSON with defined keys.
1.2 Agentforce Multi-Step Reasoning Pattern

2.1 Enterprise Rules for Agents
- Every step must have preconditions and postconditions.
- All logic must be deterministic in Apex / Flows, not generated by AI.
- Agents only recommend systems validate.
6.SDLC, Deployment & Testing Framework for Enterprise AI
1. Full SDLC for AI Components
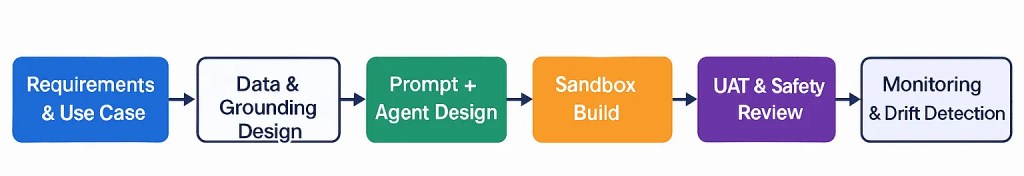
1.1 SDLC Notes
- Requirements: Business KPIs, SOPs, autonomy boundaries.
- Design: Grounding sources, templates, agent privileges.
- Build: Flows, Apex, Prompt Templates, Agent Actions.
- Testing: Simulation runs, edge cases, negative scenarios.
- Safety Review: Compliance & InfoSec sign-off.
- Enterprise Testing Strategy
2.1 Types of Tests
- Grounding Validation — Are KB/articles correct + current?
- Behavior Tests — Expected answers? Safe outputs?
- Edge Cases — Missing fields, corrupted records, conflicting inputs.
- Load & Performance — Agent execution under scale.
2.2 Data Sets for Testing
Use synthetic test records via Data Mask or custom Apex factories.
7.Monitoring, Drift Detection & Continuous Optimization
1. Observability Architecture
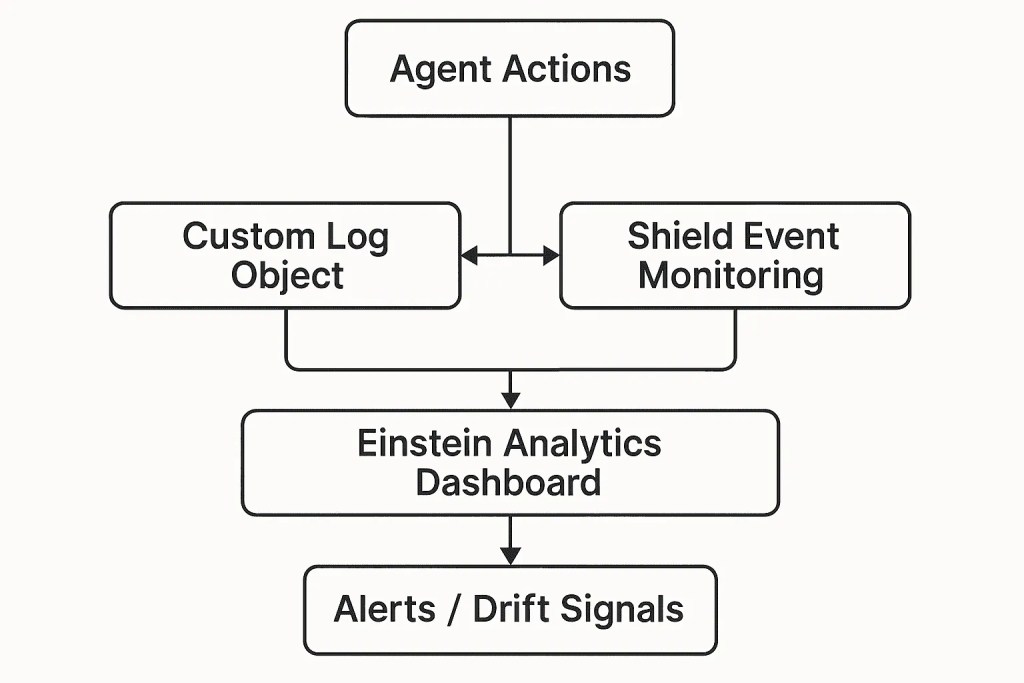
1.1 What to Monitor
- Action success/failure rates
- Escalation frequency
- Data modification accuracy
- Deviation from expected SOP behavior
- Drift Detection Framework
2.1 Drift Indicators
- Declining accuracy
- Increased manual overrides
- Sudden change in agent decisions
- Policy/SOP changes not reflected in output
2.2 Drift Remediation Cycle
- Detect via dashboards/logs
- Inspect failures
- Update grounding
- Update prompt templates
- Re-test and redeploy
8.Enterprise Rollout Strategy & Governance Model
- Enterprise Rollout Strategy
1.1 Start Small (Pilot)
- Pick 1–2 high-volume processes with low risk.
- Deploy in limited visibility groups.
1.2 Scale to Business Units
- Create reusable prompt libraries, agent patterns and action packs.
- Centralize governance via AI Center of Excellence (AI-CoE).
1.3 Organization-Wide Expansion
- Implement unified audit dashboards.
- Add multi-region SOP variants.
- Document autonomy boundaries for each agent.
- Governance Model (AI-CoE)
Roles
- AI Architect: Oversees design & guardrails.
- Data Owner: Ensures high-quality grounding.
- Security Lead: Reviews of access & PII rules.
- Release Manager: Governs deployments & approvals.
- Business Process Owner: Validates use-case outcomes.
Decision Framework
- Risk tiers (Low/Medium/High autonomy).
- Required approvals per tier.
- Mandatory human-in-loop percentage for high-risk actions.